Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Twice weekly carfilzomib is approved at two different doses, 27 mg/m2 in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, and 56 mg/m2 with dexamethasone, for the treatment of relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma (MM). To reduce the treatment burden, the phase 3 A.R.R.O.W. study compared once weekly (70 mg/m2) to twice weekly (27 mg/m2) carfilzomib in relapsed/refractory MM patients, showing that once weekly carfilzomib increased the overall response rate (ORR) and prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) as compared to the twice weekly schedule. Here we present a pooled analysis of two phase 1/2 studies to compare once vs. twice weekly carfilzomib in newly diagnosed (ND)MM patients.
METHODS: Transplant ineligible, NDMM patients enrolled in the single-arm IST-CAR 561 and IST-CAR 506 studies were pooled together. All patients received 9 28-day induction cycles of carfilzomib, either 70 mg/m2 once weekly on days 1,8,15 (IST-CAR 561) or 36 mg/m2 twice weekly on days 1,2,8,9,15,16 (IST-CAR 506), combined with cyclophosphamide (300 mg/m2 on days 1,8,15) and dexamethasone (40 mg on days 1,8,15,22). After induction, patients received maintenance with single agent carfilzomib at the same dose and schedule as induction phase, administered until progressive disease or intolerable toxicity. The primary objective was to compare PFS and overall survival (OS) from induction and maintenance, responses and rates of adverse events (AEs) with once vs. twice weekly carfilzomib.
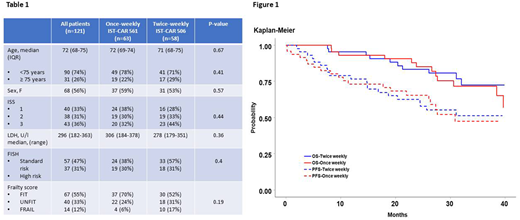
RESULTS: 121 NDMM patients (63 from IST-CAR 561 and 58 from IST-CAR 506) were analyzed. Median age at diagnosis was 72 years (IQR 68-74 years); baseline characteristics, ISS, cytogenetics by FISH and frailty status according to the IMWG frailty score, were balanced between the two groups (Table 1). After a median follow-up of 39 months, in the overall population, median PFS, PFS-2 and OS from start of induction were 36 months, 49 months and NR, respectively. No difference was observed in terms of median PFS (35.7 vs. 35.5 months; p=0.26), PFS-2 (48.6 vs. 48.5; p=0.51) and OS (49 vs. NA months; p=0.50) between patients who received once vs. twice weekly carfilzomib, irrespective of age, ISS, FISH status and frailty score (Figure 1). At cycle 9, no significant difference in the rate of ≥ partial response (PR; 87% vs. 90%; p=0.78) and ≥ near complete response (nCR; 30% vs. 47%; p=0.09) was reported in the two groups. Furthermore, the rates of patients who reduced (13% vs. 24%) or discontinued carfilzomib (27% vs. 28%) were comparable in the once vs. twice weekly carfilzomib, as were the rates of ≥1 grade 3-4 hematological (24% vs. 27%) and non-hematological (30% vs. 32%) AEs.
After the induction phase, 90 patients started carfilzomib maintenance, 47 in the once weekly group and 43 in the twice weekly group. Overall, median PFS from start of maintenance was 31 months, while median PFS-2 and OS were NR. At 3 years, no difference was observed in terms of PFS (47% vs. 51%; p=0.92), PFS-2 (65% vs. 74%; p=0.74) and OS (72% vs. 73%; p=0.71) between patients who received once vs. twice weekly carfilzomib, irrespective of age, ISS, FISH status, frailty score and best response at induction. Among patients who received maintenance, 17% of patients deepened their response. Similar rates of ≥nCR (49% vs. 60%, p=0.30) and ≥CR (30% vs. 37%; p=0.51) were observed between the once vs. twice weekly groups.
During maintenance, 26% and 16% of patients required ≥1 dose reduction of carfilzomib in the once and twice weekly carfilzomib, while 27% and 30% of patients discontinued carfilzomib due to AEs or death, respectively. The rates of ≥1 grade 3-4 hematological (0% vs. 5%) and non-hematological (19% vs. 23%) AEs were comparable within the two groups.
CONCLUSION: In patients with NDMM, once weekly carfilzomib at 70 mg/m2 and twice weekly carfilzomib at 36 mg/m2 combined with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone compared favorably with current standard of treatment. Moreover, once weekly carfilzomib administered both in the induction and maintenance phase resulted in similar PFS, PFS-2 and OS as compared to a lower (36 mg/m2), twice weekly infusion. The once weekly schedule at 70 mg/m2 was well tolerated and did not increase the risk of dose reduction or discontinuation in comparison with the twice weekly schedule at 36 mg/m2. These data support the use of triplet regimen including once weekly schedule of carfilzomib as initial treatment of MM patients in future trials.
Bringhen:Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Takeda: Consultancy; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Petrucci:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board. De Paoli:Gilead: Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board; Amgen: Other: Advisory Board; Janssen: Other: Advisory Board. Musto:Amgen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Offidani:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Board. Cavo:GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Caravita di Toritto:Johnson & Johnson: Other: Advisory Board, Travel and Accomodation EHA; Amgen: Other: Advisory Board; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Travel and Accomodation EMN; Takeda: Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board, Travel and Accomodation ASH, Research Funding. Montefusco:Janssen: Other: Advisory Board; Amgen: Other: Advisory Board; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board. Palumbo:Takeda: Employment. Boccadoro:Mundipharma: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Larocca:Janssen-Cilag: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.